Variography#
import geolime as geo
dh_tom = geo.read_file("../data/dh_tom_comp.geo")
Once the capping value determined, we can create a new property to capp the value above 25.
dh_tom.set_property(name='Zn_cap', data='Zn_pct')
dh_tom.update_property(name='Zn_cap', data='25', region="(Zn_cap > 25)")
Normal Score#
For simplicity in variography analysis, let’s compute the normal scores of the data.
gauss_score function returns a numpy array, so let’s create a new property on the Drillholes.
geo.gauss_score(dh_tom['Zn_cap'])
2026-02-05 11:17:49,062 [WARNING] GeoLime Project - |GEOLIME|.anamorphosis.py : There are NaN in data. They will be ignored.
array([-0.78162595, nan, nan, ..., -0.73537037,
-0.97667753, -1.06409047])
dh_tom.set_property(name="Zn_gauss", data=geo.gauss_score(dh_tom['Zn_cap']))
2026-02-05 11:17:49,101 [WARNING] GeoLime Project - |GEOLIME|.anamorphosis.py : There are NaN in data. They will be ignored.
Experimental Analysis#
Lag Creation#
For Variography analysis, lag creation can be perfom
implicitly with a number of lags and a length of lag
explicitly with interval values provided.
lags, tol = geo.generate_lags_from_interval([[0, 10], [10, 20], [20, 40]])
lags, tol = geo.generate_lags(lag=40, plag=50, nlags=15)
lags
array([ 0., 40., 80., 120., 160., 200., 240., 280., 320., 360., 400.,
440., 480., 520., 560.])
tol
20.0
Variography Analysis is perform in 2 step:
finding the main direction
computing the semi variogram 1D in the major/semi-major/minor directions
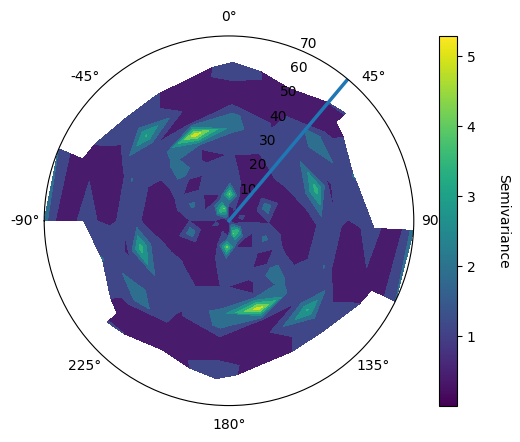
The finding of the main direction is perform through the analysis of variomap is the different planes.
Analysis around the Z axis for the azimuth using
vario_map/vario_contour;Once found the main azimuth, analysis around the X axis for the dip using
vario_contour_dip;Once found the correspond azimuth and dip, analysis around the Z axis for the pitch using
vario_contour_pitch
Finding main direction#
geo.vario_map(
geo_object=dh_tom,
attribute="Zn_gauss",
region="Zn_gauss.notna()",
lags=lags,
tol=tol,
n_az=15,
atol=15,
backend=geo.GeostatsBackend.RUST,
rust_multithread=True
)
geo.vario_contour(
geo_object=dh_tom,
attribute="Zn_gauss",
region="Zn_gauss.notna()",
lags=lags,
tol=tol,
n_az=15,
atol=10,
user_azimuth=145,
backend=geo.GeostatsBackend.RUST,
rust_multithread=True
)
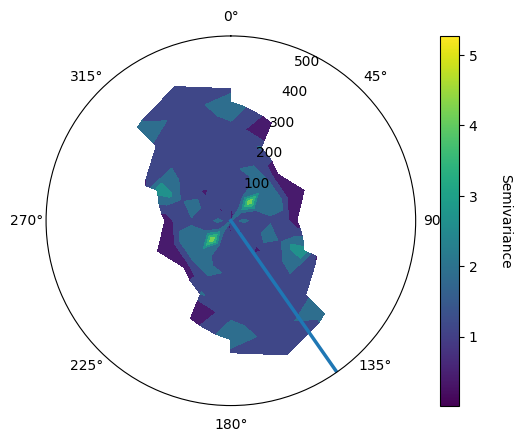
geo.vario_contour_dip(
geo_object=dh_tom,
attribute="Zn_gauss",
region="Zn_gauss.notna()",
lags=lags,
tol=tol,
azimuth=145,
n_dip=18,
atol=10,
user_dip=30,
c_step=None,
save_file=None,
backend=geo.GeostatsBackend.RUST,
rust_multithread=True
)
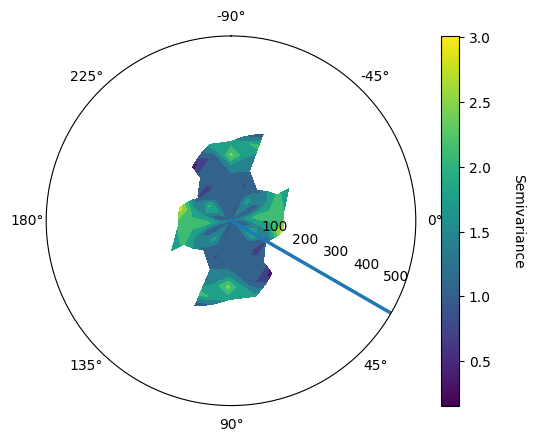
lags, tol = geo.generate_lags(lag=5, plag=50, nlags=15)
geo.vario_contour_pitch(
geo_object=dh_tom,
attribute="Zn_gauss",
region="Zn_gauss.notna()",
lags=lags,
tol=tol,
azimuth=145,
dip=30,
n_pitch=15,
atol=10,
user_pitch=40,
c_step=None,
save_file=None,
backend=geo.GeostatsBackend.RUST,
rust_multithread=True
)
Computing Major/Semi-major/minor 1D variograms#
lags, tol = geo.generate_lags(lag=40, plag=50, nlags=15)
vario_exp_major = geo.variogram(
object=dh_tom,
attribute="Zn_gauss",
region="Zn_gauss.notna()",
geographic_azimuth=145,
dip=30,
pitch=40,
lags=lags,
tol=tol,
atol=15
)
vario_exp_major
| lag | npairs | avgdist | vario | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0.0 | 77.0 | 7.075251 | 0.465396 |
| 1 | 40.0 | 3398.0 | 40.792308 | 0.777796 |
| 2 | 80.0 | 40960.0 | 78.978514 | 0.806629 |
| 3 | 120.0 | 30230.0 | 124.930330 | 0.990211 |
| 4 | 160.0 | 40894.0 | 156.149538 | 1.115701 |
| 5 | 200.0 | 36094.0 | 203.015277 | 1.081183 |
| 6 | 240.0 | 25161.0 | 236.455210 | 1.035988 |
| 7 | 280.0 | 33921.0 | 281.398117 | 0.942194 |
| 8 | 320.0 | 37335.0 | 321.020570 | 1.038284 |
| 9 | 360.0 | 25134.0 | 358.368372 | 0.778095 |
| 10 | 400.0 | 26563.0 | 400.087531 | 0.820317 |
| 11 | 440.0 | 23755.0 | 437.475481 | 0.803660 |
| 12 | 480.0 | 16474.0 | 482.005500 | 0.954571 |
| 13 | 520.0 | 15733.0 | 520.853958 | 0.870347 |
| 14 | 560.0 | 15398.0 | 559.318854 | 0.754568 |
geo.plot_semivariogram(
variograms=[vario_exp_major],
display_npairs=True
)
vario_exp_semi_major = geo.variogram(
object=dh_tom,
attribute="Zn_gauss",
region="Zn_gauss.notna()",
geographic_azimuth=145,
dip=30,
pitch=-50,
lags=lags,
tol=tol,
atol=15
)
geo.plot_semivariogram(
variograms=[vario_exp_semi_major],
display_npairs=True
)
lags, tol = geo.generate_lags(lag=2, plag=50, nlags=15)
vario_exp_minor = geo.variogram(
object=dh_tom,
attribute="Zn_gauss",
region="Zn_gauss.notna()",
geographic_azimuth=145,
dip=-60,
pitch=40,
lags=lags,
tol=tol,
atol=30
)
geo.plot_semivariogram(
variograms=[vario_exp_minor],
display_npairs=True
)
Computing Downhole Variogram#
lags, tol = geo.generate_lags(lag=1., plag=50, nlags=20)
vario_exp_bh = geo.variogram_downhole(
object= dh_tom,
attribute="Zn_gauss",
region="Zn_gauss.notna()",
lags=lags,
tol=tol,
)
geo.plot_semivariogram(
variograms=[vario_exp_bh],
display_npairs=True
)
Automatic Fitting#
Automatic Fitting uses an empty model to fit along experimental variograms. Fitting is usually performed in 2 steps : first fit the nugget and then fit the other structures.
Fitting the Nugget#
nugget_model = geo.Nugget() + geo.Spherical()
The fitting algorithm can be set up to preferrentially fit the small ranges using the INVERSE_DISTANCE or SQUARED_INVERSE_DISTANCE.
geo.model_fit(
variograms=[vario_exp_bh],
cov=nugget_model,
weighting_method=geo.VarioFitWeightingMethod.SQUARED_INVERSE_DISTANCE
)
print(nugget_model)
Model with 2 components
Component 1 :
Sill : 0.027873319034633838
Covariance type : Nugget
Component 2 :
Sill : 0.6725687077193347
Covariance type : Spherical
Scales : (8.68655231153718, 4.750030928607003, 6.534127102914507)
Angles : (171.47734374796926, 7.785339845394673e-11, 78.85078577685731)
Total sill = 0.7004420267539686
Model and experimental variogram can be plotted on the same graphic by specifying the parameter model and model_angles. Note that for downhole varigram the model_angles values do not have any importance.
geo.plot_semivariogram(
variograms=[vario_exp_bh],
model=nugget_model,
model_angles=[{"azi":0, "dip":90, "pitch":90}],
display_npairs=True
)
Each structure component can be accessed using the cov_elem_list attribute.
nugget_model.cov_elem_list[0].sill
0.027873319034633838
Fitting the structures#
model = geo.Nugget() + geo.Spherical() + geo.Spherical()
short_range_spherical_ratio = 0.6
long_range_spherical_ratio = 0.4
geo.model_fit(
variograms=[
vario_exp_major,
vario_exp_semi_major,
vario_exp_minor
],
cov=model,
constraints=[
{"sill_fixed":0.13},
{
"sill_max": short_range_spherical_ratio * (vario_exp_major.attrs["variable_var"] - 0.13),
"angle_fixed_0": 145,
"angle_fixed_1": 60,
"angle_fixed_2": 40,
"scale_max_0":100,
"scale_max_1":100,
"scale_max_2":20
},
{
"sill_max": long_range_spherical_ratio * (vario_exp_major.attrs["variable_var"] - 0.13),
"angle_fixed_0": 145,
"angle_fixed_1": 60,
"angle_fixed_2": 40,
}
]
)
geo.plot_semivariogram(
variograms=[vario_exp_major, vario_exp_semi_major, vario_exp_minor],
model=model,
model_angles=[
{"azi":145, "dip":60, "pitch":40},
{"azi":145, "dip":60, "pitch":-50},
{"azi":145, "dip":-30, "pitch":40},
],
display_npairs=True
)
print(model)
Model with 3 components
Component 1 :
Sill : 0.13
Covariance type : Nugget
Component 2 :
Sill : 0.5420557387573294
Covariance type : Spherical
Scales : (3.926935518640417, 85.71917052844384, 9.781965936798198)
Angles : (145.0, 60.0, 40.0)
Component 3 :
Sill : 0.36137049661196347
Covariance type : Spherical
Scales : (559.5580933527096, 13.991551321339147, 559.4463109309288)
Angles : (145.0, 60.0, 40.0)
Total sill = 1.033426235369293
dh_tom.to_file("../data/dh_tom_comp_capped.geo")